What Is a Bond Yield?
A bond yield refers to the return an investor receives from holding a bond. Bonds are fixed-income securities issued by governments or corporations to raise capital. In Canada, government bonds, especially the 5-year bond, are closely monitored as they are tied directly to mortgage rates. When bond yields rise or fall, mortgage rates tend to follow suit.How Do Bond Yields Influence Mortgage Rates?
Mortgage rates in Canada, particularly fixed-rate mortgages, are often influenced by government bond yields. The most common bonds tied to mortgage rates are the 5-year and 10-year government bonds. Here’s how it works:- When Bond Yields Increase: Lenders adjust their mortgage rates higher to match the increase in yields. This adjustment ensures that their mortgage products remain profitable.
- When Bond Yields Decrease: Lenders may reduce mortgage rates to align with lower bond yields, providing a more competitive offering for borrowers.
Example of Bond Yield Impact on Mortgage Rates
Consider a scenario where the 5-year bond yield is currently at 2%. If the yield rises to 2.5%, lenders might increase their 5-year fixed mortgage rate from 4.5% to 5% to maintain a profitable margin. Similarly, if the bond yield drops to 1.5%, lenders may lower their rates to 4%, offering cheaper borrowing options to homeowners. For example:| Bond Yield | Mortgage Rate (5-Year Fixed) |
|---|---|
| 2.0% | 4.5% |
| 2.5% | 5.0% |
| 1.5% | 4.0% |
Why Bond Yields and Mortgage Rates Are Closely Tied
Lenders use bond yields as a benchmark for setting their mortgage rates because bonds and mortgages are both forms of debt securities. Both instruments react similarly to changes in economic conditions and central bank policies. For example, if the Bank of Canada raises interest rates to curb inflation, bond yields generally rise, leading to higher mortgage rates. Conversely, when the central bank lowers rates, bond yields typically fall, resulting in lower mortgage rates.Chart: Bond Yields vs. Mortgage Rates Over Time
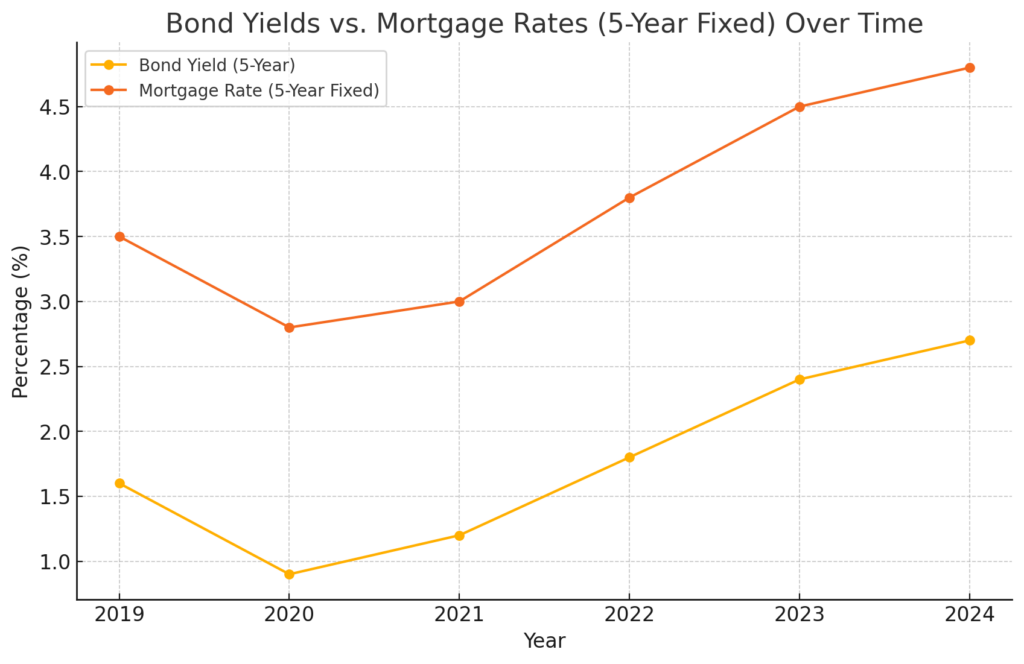
Figure: Bond Yields vs. Mortgage Rates (5-Year Fixed) Over Time
How to Track Bond Yields and Mortgage Rates
To stay informed, potential homebuyers and investors should monitor the Bank of Canada’s bond yield rates and the latest mortgage rates from leading lenders. This can help you anticipate changes in the housing market and plan your mortgage strategy accordingly.Conclusion: Stay Informed About Bond Yields
Understanding the link between bond yields and mortgage rates in Canada is crucial for anyone considering buying a home or refinancing an existing mortgage. By monitoring bond yields, you can better predict mortgage rate movements and make more informed financial decisions. Keep an eye on bond yields, stay updated on market conditions, and consult with financial professionals to find the best mortgage rate options available.FAQ
Bond yields, especially the 5-year government bond yield, serve as a benchmark for lenders. When bond yields rise, mortgage rates tend to increase as well, and when they fall, mortgage rates usually decrease.
Lenders use bond yields because both bonds and mortgages are debt securities. Bond yields react to economic conditions and central bank policies, making them a reliable indicator for predicting mortgage rate changes.
Mostly fixed mortgage rates are influenced by bond yields. Variable mortgage rates, on the other hand, are typically linked to the prime rate, which is influenced by the Bank of Canada’s interest rate decisions.
Yes, keeping an eye on the 5-year government bond yield can help you anticipate changes in 5-year fixed mortgage rates, allowing you to time your mortgage applications or renewals better.
If bond yields are rising, it may be wise to lock in a fixed mortgage rate before rates increase further. Consult with your mortgage advisor to explore the best options based on current bond yield trends.